
In the computer game industry, GPUs are used for graphics rendering, and for game physics calculations (physical effects such as debris, smoke, fire, fluids) examples include PhysX and Bullet. Third party wrappers are also available for Python, Perl, Fortran, Java, Ruby, Lua, Common Lisp, Haskell, R, MATLAB, IDL, Julia, and native support in Mathematica. In addition to libraries, compiler directives, CUDA C/C++ and CUDA Fortran, the CUDA platform supports other computational interfaces, including the Khronos Group's OpenCL, Microsoft's DirectCompute, OpenGL Compute Shader and C++ AMP. Fortran programmers can use 'CUDA Fortran', compiled with the PGI CUDA Fortran compiler from The Portland Group. C/C++ programmers can use 'CUDA C/C++', compiled to PTX with nvcc, Nvidia's LLVM-based C/C++ compiler, or by clang itself.
#Cmake cuda software#
The CUDA platform is accessible to software developers through CUDA-accelerated libraries, compiler directives such as OpenACC, and extensions to industry-standard programming languages including C, C++ and Fortran. Copy the resulting data from GPU memory to main memory.GPU's CUDA cores execute the kernel in parallel.Copy data from main memory to GPU memory."SP", "streaming processor", "cuda core", but these names are now deprecated)Īnalogous to individual scalar ops within a vector op Simultaneous call of the same subroutine on many processors The following table offers a non-exact description for the ontology of CUDA framework. This design is more effective than general-purpose central processing unit (CPUs) for algorithms in situations where processing large blocks of data is done in parallel, such as: By 2012, GPUs had evolved into highly parallel multi-core systems allowing efficient manipulation of large blocks of data. The graphics processing unit (GPU), as a specialized computer processor, addresses the demands of real-time high-resolution 3D graphics compute-intensive tasks. When it was first introduced, the name was an acronym for Compute Unified Device Architecture, but Nvidia later dropped the common use of the acronym.įurther information: Graphics processing unit
#Cmake cuda code#
CUDA-powered GPUs also support programming frameworks such as OpenMP, OpenACC and OpenCL and HIP by compiling such code to CUDA.ĬUDA was created by Nvidia. This accessibility makes it easier for specialists in parallel programming to use GPU resources, in contrast to prior APIs like Direct3D and OpenGL, which required advanced skills in graphics programming. ĬUDA is designed to work with programming languages such as C, C++, and Fortran. CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements, for the execution of compute kernels. Tried with: CMake 2.8.7, CUDA 5.0 and Ubuntu 12.CUDA (or Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for general purpose processing, an approach called general-purpose computing on GPUs ( GPGPU). This is a known limitation of the CUDA module of CMake currently. Note: Include directories cannot be specified for a particular target using target_include_directories. This does not cause any problems, just something you might need to be aware of.įor information about other CMake commands for CUDA see the file /usr/share/cmake-2.8/Modules/FindCUDA.cmake and the files inside /usr/share/cmake-2.8/Modules/FindCUDA/. The behavior of the Makefile generated by CMake is slightly different: it calls the default C++ compiler for.
Typically nvcc calls both the host compiler and device compiler by itself on both. # Specify target & libraries to link it with # Specify target & source files to compile it from
#Cmake cuda how to#
The CMakeLists.txt shown below is an example of how to configure all these features: # CMakeLists.txt for CUDA
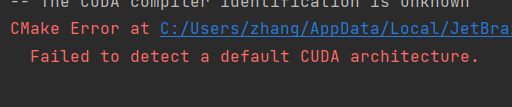
Steps to build and run program on Linux: $ mkdir buildĪny non-trivial CUDA program will need special compilation flags, include directories, library directories and multiple source files. On Windows, cmake would generate a Visual Studio solution, that can be used to build the code. To build our program on Linux, we first run cmake to generate a Makefile and use that Makefile to build and run. # Specify binary name and source file to build it from To build this using CMake, we create a file named CMakeLists.txt containing these lines: # CMakeLists.txt to build hellocuda.cu Let us assume that we want to build a CUDA source file named src/hellocuda.cu. CMake has support for CUDA built in, so it is pretty easy to build CUDA source files using it. 📅 2013-Sep-13 ⬩ ✍️ Ashwin Nanjappa ⬩ 🏷️ cmake, cuda, make ⬩ 📚 ArchiveĬMake is a popular option for cross-platform compilation of code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
